Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
Editorials & Other Articles
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
Science
Related: About this forumNASA Detects More Than 50 Methane 'Super-Emitter' Zones Around The World
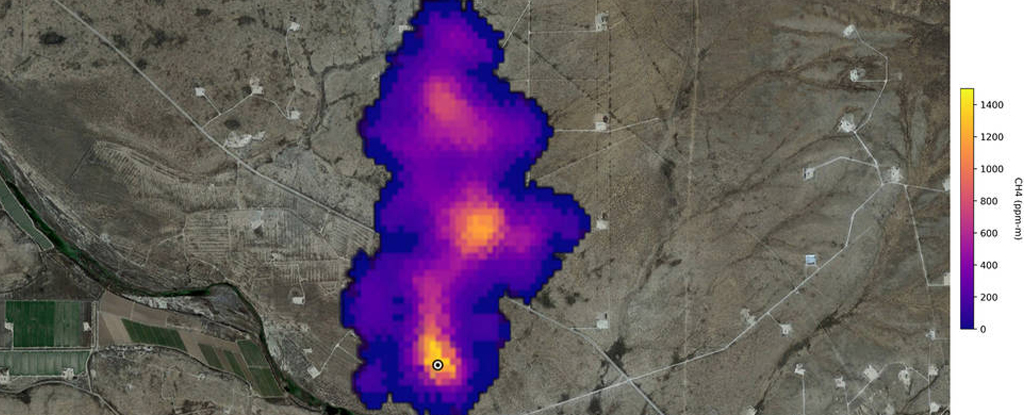
A 3 km methane plume detected by NASA’s Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation mission, southeast of Carlsbad, New Mexico. (NASA/JPL-Caltech)
NASA scientists, using a tool designed to study how dust affects climate, have identified more than 50 spots around the world emitting major levels of methane, a development that could help combat the potent greenhouse gas. "Reining in methane emissions is key to limiting global warming," NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said in a press release on Tuesday. "This exciting new development will not only help researchers better pinpoint where methane leaks are coming from, but also provide insight on how they can be addressed – quickly."
NASA said its Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) is designed to foster understanding of the effects of airborne dust on climate. But EMIT, which was installed on the International Space Station in July and can focus on areas as small as a soccer field, has also shown the ability to detect the presence of methane.
NASA said more than 50 "super-emitters" of methane gas in Central Asia, the Middle East, and the southwestern United States have been identified so far. Most of them are connected to the fossil-fuel, waste or agriculture sectors. Kate Calvin, NASA's chief scientist and senior climate advisor, said EMIT's "additional methane-detecting capability offers a remarkable opportunity to measure and monitor greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change."
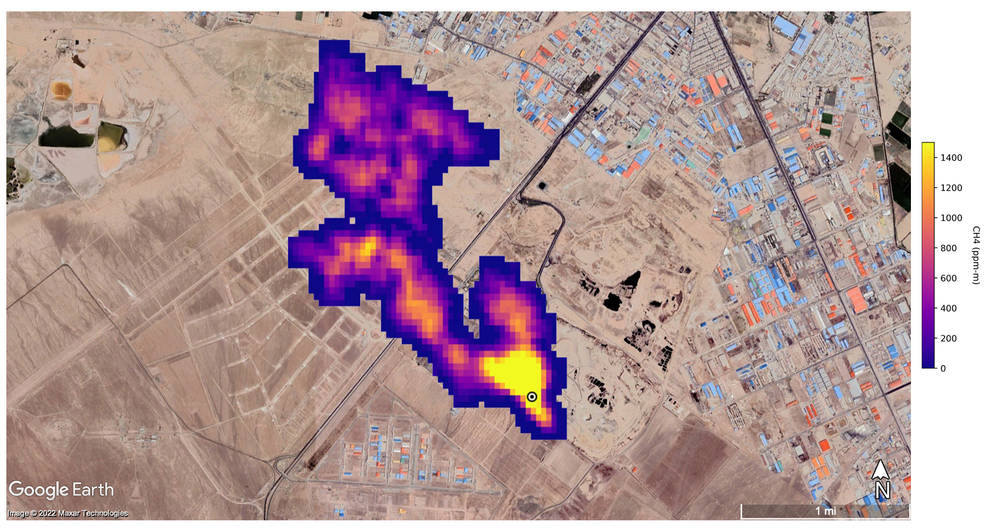
A 4.8 kilometer long methane plume south of Tehran, Iran. (NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Methane is responsible for roughly 30 percent of the global rise in temperatures to date. While far less abundant in the atmosphere than CO2, it is about 28 times more powerful as a greenhouse gas on a century-long timescale. Over a 20-year time frame, it is 80 times more potent. Methane lingers in the atmosphere for only a decade, compared to hundreds or thousands of years for CO2. This means a sharp reduction in emissions could shave several tenths of a degree Celsius off of projected global warming by mid-century, helping keep alive the Paris Agreement goal of capping Earth's average temperature increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius, according to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
https://www.sciencealert.com/nasa-detects-more-than-50-methane-super-emitter-zones-around-the-world
4 replies
 = new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
= new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
NASA Detects More Than 50 Methane 'Super-Emitter' Zones Around The World (Original Post)
milestogo
Oct 2022
OP
Backseat Driver
(4,642 posts)1. Wow, a Universal Space Dust and Cow Fart Detector...
= We got cows!
OK - too much silliness for a fascinating helpful tool?
OK - too much silliness for a fascinating helpful tool?
underpants
(187,620 posts)2. On Earth that's called taco Tuesday
packman
(16,296 posts)3. Or a Trump rally
DBoon
(23,206 posts)4. I bet they could find my dog with that instrument